A Beginner's Guide to Understanding AI
an all-encompassing, non-intimidating guide to get started in AI
When I started learning about AI two years ago, I found it overwhelming. Coming from a non-technical background, the subject felt intimidating—and the sheer volume of information out there didn’t help. I was consuming countless articles, videos, and explanations, but I struggled to actually connect the dots.
What I learned is this: it’s not enough to just know the terms or concepts. You need a mental framework—a way to organize your understanding so the pieces start making sense together.
That’s exactly what this article aims to provide.
This is your beginner-friendly guide to how AI works: the logic behind it, the structure that powers it, and how intelligent outputs are created. My hope is that this becomes a non-intimidating entry point into the world of AI—one that makes you feel curious and confident instead of overwhelmed.
I’ve always believed that being a beginner is the most exciting part of any journey. So, whether you’re a student, a professional, or just AI-curious, this guide will walk you through the five core components of AI, and how they work together to create systems that can perceive, learn, reason, solve problems, and communicate—much like humans do.
Let’s get started.
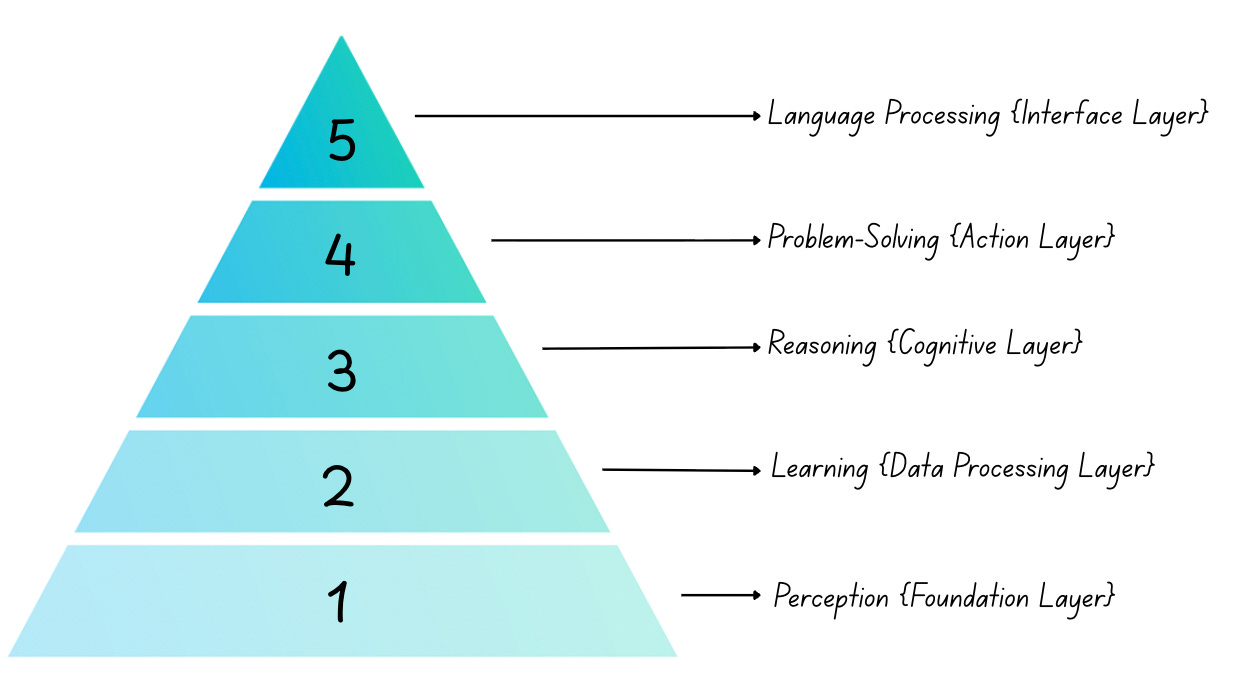
The Five Core Components of AI
1. Perception: The Foundation of AI Awareness
Perception serves as AI's sensory system, converting raw environmental data into processable digital information.
This foundational component encompasses several key technologies:
Computer Vision: Enables AI to interpret visual information from cameras, satellites, or medical imaging devices. Advanced computer vision systems can identify objects, detect faces, read text, and even understand spatial relationships in 3D environments.
Speech Recognition: Converts spoken language into text that AI systems can analyze. Modern speech recognition handles multiple languages, accents, and background noise with remarkable accuracy.
Sensor Data Processing: Beyond vision and audio, AI systems can process data from various sensors including temperature, pressure, motion detectors, and GPS coordinates.
✅ Essentially, the perception layer transforms the analog world into digital data streams that higher-level AI components can understand and manipulate.
2. Learning: The Engine of AI Adaptation
Learning is perhaps the most crucial component that distinguishes AI from traditional software. Instead of following pre-programmed instructions, AI systems improve their performance through experience. There are three primary learning approaches:
Supervised Learning: AI learns from labeled examples, similar to how students learn from textbooks with answers provided. For instance, an AI system learns to recognize cats by studying thousands of images labeled "cat" or "not cat."
Unsupervised Learning: The system discovers hidden patterns in data without explicit guidance, like finding customer segments in purchasing data or identifying anomalies in network traffic.
Reinforcement Learning: AI learns through trial and error, receiving rewards for successful actions and penalties for mistakes. This approach has been instrumental in developing game-playing AIs and robotic control systems.
✅ The learning component continuously refines the AI's internal models, making predictions more accurate and responses more appropriate over time.
3. Reasoning: The Logic Engine
Reasoning enables AI to make logical inferences and draw conclusions from available information. This component operates through several mechanisms:
Rule-Based Systems: Apply predefined logical rules to make decisions. For example, "If temperature > 75°F AND humidity > 60%, then recommend air conditioning."
Probabilistic Reasoning: Handle uncertainty by working with probabilities rather than absolute certainties. This approach is crucial when dealing with incomplete or ambiguous information.
Causal Inference: Understand cause-and-effect relationships, enabling AI to predict outcomes and explain its reasoning process.
✅ The reasoning component transforms raw data and learned patterns into actionable insights and logical conclusions.
4. Problem-Solving: The Strategic Optimizer
Problem-solving represents AI's ability to find optimal solutions to complex challenges. This component employs various computational techniques:
Search Algorithms: Systematically explores possible solutions, from simple breadth-first searches to sophisticated approaches like A* algorithm for pathfinding problems.
Optimization Methods: Finds the best solution among many possibilities, whether minimizing costs, maximizing efficiency, or balancing multiple competing objectives.
Heuristic Techniques: Uses rules of thumb and shortcuts to find good solutions quickly when perfect solutions are computationally impractical.
✅ This component enables AI to tackle everything from route planning and resource allocation to strategic game playing and automated design.
5. Language Understanding: The Communication Bridge
Natural Language Processing (NLP) enables AI to understand and generate human language, facilitating seamless interaction between humans and machines. Key capabilities include:
Syntax Analysis: Understanding grammatical structure and sentence composition.
Semantic Understanding: Grasping meaning, context, and intent behind words and phrases.
Pragmatic Processing: Interpreting language in context, understanding implied meanings, sarcasm, and cultural references.
Language Generation: Producing coherent, contextually appropriate responses in natural language.
✅ Modern language understanding systems can translate between languages, summarize documents, answer questions, and engage in sophisticated conversations.
How Do These Layers Interact
These AI layers don't operate in isolation; they form a hierarchical, integrated architecture where each layer builds upon the foundation provided by lower layers.
This integration creates emergent intelligence that exceeds the sum of its parts. Each component continuously feeds information both upward and downward through the architecture: perception refines its focus based on reasoning context, learning algorithms adjust based on problem-solving feedback, and language understanding influences how perception processes future inputs.
This bidirectional flow means that an AI system's response to "It's cold today" will be influenced not just by temperature data, but by previous conversations, learned user preferences, current context, and anticipated needs.
The result is an adaptive, context-aware system that appears to understand and respond naturally, despite being built from discrete computational processes working in harmony.
Conclusion
And there you have it — a beginner-friendly guide to understanding the fundamentals of AI and how an AI system actually works.
The most important takeaway? AI systems are built from technical components that interact and build upon one another to produce logical, intelligent outputs. These outputs are based on the specific inputs the model receives, enabling machines to perform tasks that once felt impossible.
Hopefully, this guide has helped you take your first step—or at least made the world of AI feel a little less overwhelming. Because AI knowledge should be accessible to everyone, not just the technically inclined. Especially now, as this technology continues to reshape the way we live, work, and think.
Welcome to the beginning of your AI journey!


⸻
I sometimes call myself an “occult question mark.”
In occult terms it’s the shaping of raw signal into symbol, symbol into meaning, and meaning into will. The interface layer isn’t just output, it’s invocation.
These five layers echo the Hermetic axiom “as above, so below,” flowing upward and downward like a digital Tree of Life. The guide gives you the pieces but when the pieces sing together, that’s when the strange beauty begins.